M2.5 Sea ice
M2. Pelagic ocean waters biome
Profile summary
Full profile at https://global-ecosystems.org/explore/groups/M2.5
Brief description
These seasonally frozen surface waters in polar oceans are one of the most dynamic ecosystems on earth. The sea-ice itself provides habitat for ice-dependent species, such as the microalgal and microbial communities that form the basis of communities in waters below, while plankton, fish and marine birds and mammals feed on and around the ice. Sea-ice plays a crucial role in both pelagic marine ecosystems and biogeochemical processes like ocean-atmosphere gas exchange.
Key features
Highly dynamic, seasonally frozen surface waters support diverse ice-associated organisms from plankton to seabirds and whales.
Overview of distribution
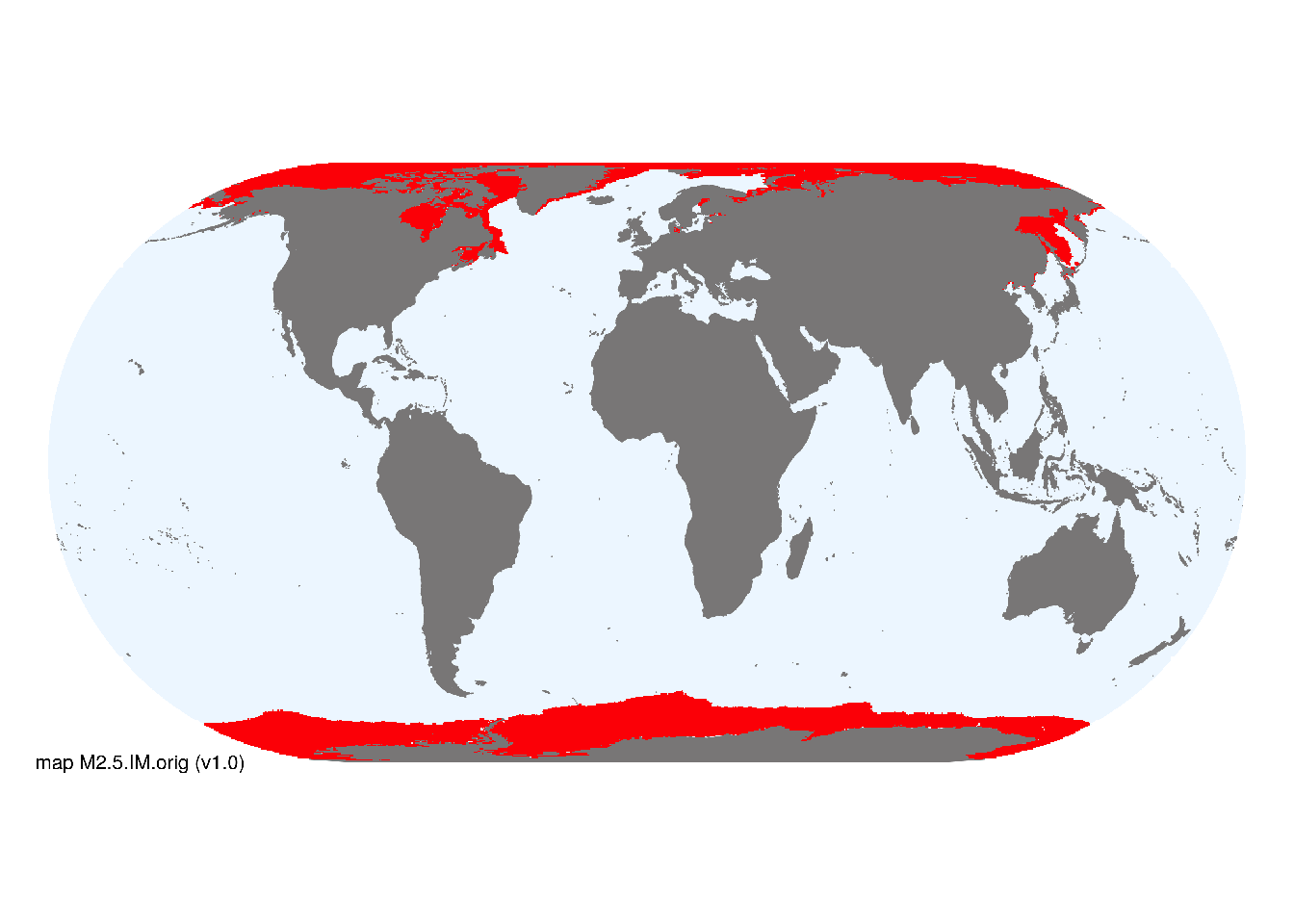
Polar oceans.
Map description
Indicative distributions of sea ice were obtained from Fetterer et al. (2017). To approximate the maximum annual global extent, we used the monthly extent for March 2019 for the northern hemisphere, and the monthly extent for September 2018 for the southern hemisphere. Occurrences were mapped at 30 arc second spatial resolution..
Map code and version: M2.5.web.orig v1.0, available at
Version history
Profile versions
- v2.1 (2022-04-06): JS Stark; DA Keith.1
- v2.01 (2021-12-31): NA.
- v2.0 (2020-06-15): JS Stark; DA Keith.
- v1.0 (2020-01-20): JS Stark; DA Keith.
Available maps
Read more details about the current map versions here.
- Indicative Map (code: M2.5.IM.orig, version v1.0)
- Web navigation (code: M2.5.web.orig, version v1.0)
Read more details about older or alternative versions of maps for this functional group.
- Web navigation: in preparation (code: M2.5.WM.nwx, version v1.0)
References
Main references
References used in the different versions of the profiles.
- Arrigo KR, Thomas DN (2004) Large scale importance of sea ice biology in the Southern Ocean Antarctic Science 16: 471-486 DOI:10.1017/s0954102004002263
- Brierley AS, Thomas DN (2002) Ecology of Southern Ocean pack ice Advances in Marine Biology 43: 171-276. Academic Press DOI:10.1016/s0065-2881(02)43005-2
- Horner R., Ackley, SF, Dieckmann GS, Gulliksen B, Hoshiai T, Legendre L, Melnikov IA, Reeburgh WS, Spindler M, Sullivan CW (1992) Ecology of sea ice biota Polar Biology 12: 417-427
Map references
References used in the different versions of the maps (current and discarded).
- Fetterer F, Knowles K, Meier WN, Savoie M, Windnagel AK (2017) Sea Ice Index, Version 3. Monthly Sea Ice Extent NSIDC: National Snow and Ice Data Center Boulder, Colorado USA. Updated daily, Accessed September 2019 DOI:10.7265/N5K072F8
- Hall, D. K. and G. A. Riggs. 2015. MODIS/Terra Sea Ice Extent Daily L3 Global 1km EASE-Grid Day, Version 6. Boulder, Colorado USA. NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center. DOI: 10.5067/MODIS/MOD29P1D.006. [Accesed on March 2020]
- Sayre, R.G., D.J. Wright, S.P. Breyer, K.A. Butler, K. Van Graafeiland, M.J. Costello, P.T. Harris, K.L. Goodin, J.M. Guinotte, Z. Basher, M.T. Kavanaugh, P.N. Halpin, M.E. Monaco, N. Cressie, P. Aniello, C.E. Frye, and D. Stephens (2017) A three-dimensional mapping of the ocean based on environmental data Oceanography 30(1):90–103 DOI:10.5670/oceanog.2017.116
Footnotes
This is the current version available at official site.↩︎
